Not known Details About Residential Water Treatment System
Table of ContentsThe Only Guide for Residential Water Treatment System5 Simple Techniques For Residential Water Treatment System3 Easy Facts About Residential Water Treatment System ExplainedThings about Residential Water Treatment System
5)5. 1 The demand for large-scale water therapy, Water treatment is the procedure of eliminating all those substances, whether organic, chemical or physical, that are potentially harmful in water supply for human as well as residential use. This therapy assists to generate water that is safe, tasty, clear, colourless and odourless. Water likewise requires to be non-corrosive, meaning it will certainly not create damage to pipework.This creates a demand for huge quantities of secure water to be supplied dependably and also consistently, as well as this need is growing. As city populations increase, there is a need to locate brand-new sources to fulfill the growing demand. If groundwater is readily available this can frequently be made use of with very little therapy however any surface water resource will certainly need to be treated to make it secure.
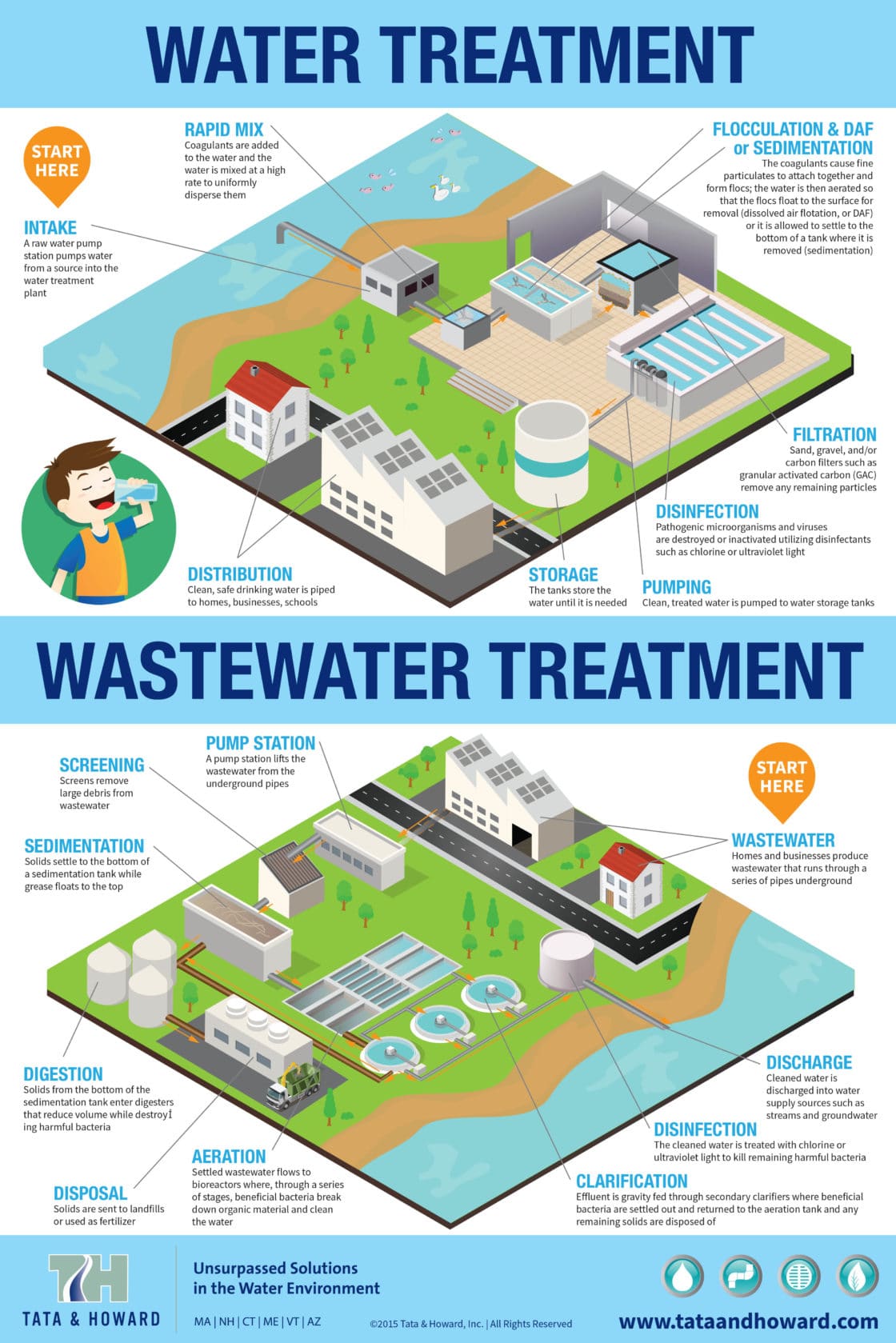
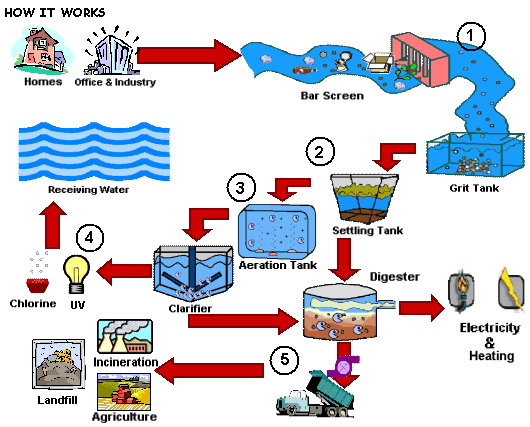
6 clarifies how this estimation is made but initially you will consider the main phases in the water therapy procedure. 5. 2 Phases in large water therapy, There are frequently seven steps (Number 5. 2) in massive water treatment for metropolitan municipal water system (Abayneh, 2004). Each of the actions will certainly be explained subsequently in this area.
Some Known Factual Statements About Residential Water Treatment System
Below the water is gently stirred by paddles in a flocculation container (Figure 5. 5) and the flocs enter into contact with each other to create bigger flocs. The flocculation basin usually has a variety of compartments with decreasing blending rates as the water advancements via the container (Figure 5.
6(b)) for a number of hours for sedimentation to happen. The material gathered at the base of the storage tank is called sludge; this is removed for disposal. 5.2. 5 Filtration, Filtering is the process where solids are divided from a liquid. In water therapy, the solids that are not separated out in the sedimentation storage tank are eliminated by passing the water with beds of sand and crushed rock.
7), with a flow rate of 48 cubic metres per square metre of filter surface per hour (this is composed as 48 m3 m2 h1) are typically used. When the filters have plenty of caught solids, they are backwashed. In this procedure, clean water and air are pumped backwards up the filter to displace the caught contaminations, and also the water lugging the dirt (described as backwash) is pumped into the sewage system, if there is one.
6 Chlorination, After sedimentation, the water is sanitized to eliminate any type of remaining pathogenic micro-organisms. The most commonly utilized anti-bacterial (the chemical utilized for sanitation) is chlorine, in the kind of a fluid (such as salt hypochlorite, Na, OCl) or a gas.
Indicators on Residential Water Treatment System You Should Know
The amount of chlorine left after this is called recurring chlorine. This stays in the water right via the distribution system, shielding it from any type of micro-organisms that might enter it, up until the water gets to the customers. World Health And Wellness Company Standards (WHO, 2003) suggest a maximum recurring chlorine of 5 mg l1 of water.

7 Supplementary therapy, Auxiliary therapy may in some cases be needed for the benefit of the population. One such circumstances is the fluoridation of water, where fluoride is included to water. It has been stated by the Globe Health And Wellness Company that 'fluoridation of water products, where possible, is the most reliable public health and wellness step for the avoidance of oral degeneration' (WHO, 2001).
The Greatest Guide To Residential Water Treatment System
5 mg l1. What does excess fluoride in the water bring about? As mentioned in Study Session 2, in kids it can trigger spotting of teeth as well as extended direct exposure can create skeletal fluorosis and also debilitating. In such high-fluoride locations, elimination or decrease of fluoride (described defluoridation) is necessary. The most basic way of doing this is to blend the high-fluoride water with water that has no (or very little) fluoride so that the final mix is risk-free - residential water treatment system.
The two chemicals are added to and swiftly blended with the fluoride-contaminated water and after that the water is mixed gently. 5.3 Management of wastes from water treatment plants, From the water therapy process that you have actually just researched, make a listing of the different wastes that arise.
In the last it is included in the inbound sewage, where it can aid negotiation of solids. The backwash from the sand filter is discharged right into the drain or returned to the river after negotiation of solids. Product packaging waste such as chemical drums can be gone back to the provider for reuse.
5.4 Sustainability as well as resilience in water therapy, In Research study Session 4 you review some factors that can influence the sustainability of a water resource. For example, lowering soil erosion by growing trees as well as preserving greenery can lower the amount of silt that collects in a storage tank and extend its life.